-
Products
-
-
-
-
Contact Us
Difference between pressure sensor and pressure transmitter
2020-11-17
While pressure sensors and pressure transmitters have similar names, they differ significantly in their applications, structures, and components.
Pressure sensors are one of the most commonly used sensors in industrial practice. They are widely used in various industrial automation environments, including water conservancy and hydropower, rail transportation, smart buildings, production automation, aerospace, military industry, petrochemicals, oil wells, power, shipbuilding, machine tools, and pipelines.
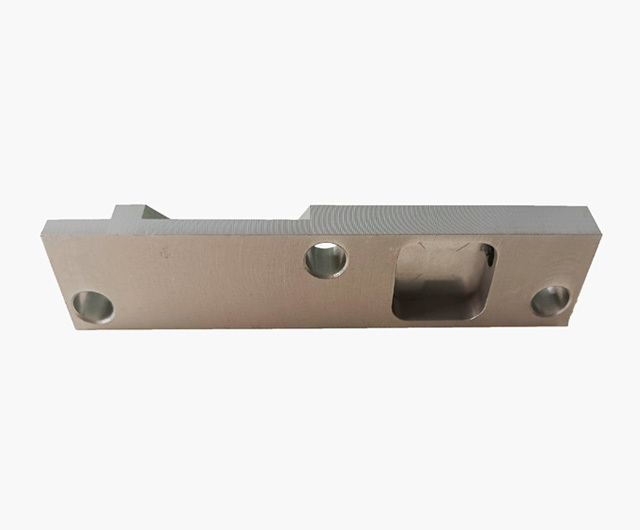
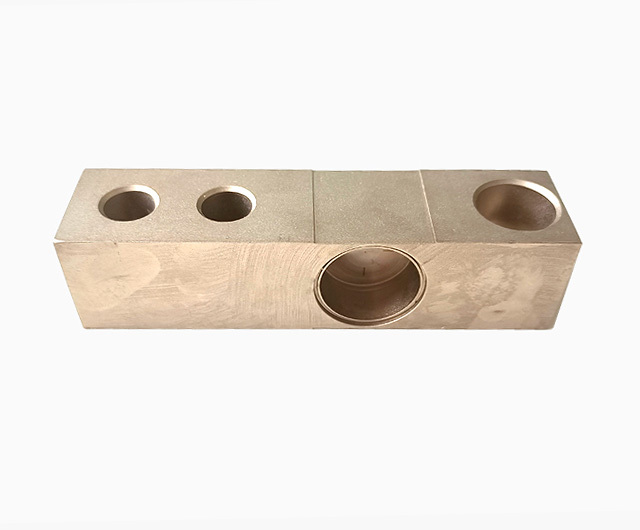
A pressure transmitter mainly consists of three parts: a pressure sensing element, a measuring circuit, and process connectors. It is widely used in the petroleum, chemical, power, city gas, pulp and paper, machinery, and shipbuilding industries.
Pressure sensors usually refer to component-level products with non-standard mV signal outputs. They are the core components of pressure transmitters. Due to the non-standard nature of the signal, users need to perform pressure calibration and design special signal processing circuits; due to the weak signal, amplifiers need to be added when the distance is long.
Pressure transmitters can also be considered pressure sensors in a literal sense, but their output signals are standard and commonly used, such as 4~20mA, 1~5V, etc., allowing for long-distance transmission.
Previous page


Hotline

Technical Support


Address
No. 1, Building 1, Yin Cang Road, Green Industry Cluster, Quzhou City, Zhejiang Province
Follow us



Copyright © 2024 Zhejiang Nan Hua Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. | Powered by www.300.cn